AI Crawling now makes up to 20% of Googlebot’s crawl activity. AI crawlers like OpenAI’s GPTBot and Anthropic’s Claude generate close to 1 billion requests each month across the web.
Your website might be invisible to AI-powered search tools if you block these crawlers, use improper markup, or have slow-loading pages. You could miss significant visibility opportunities without a proper technical setup and structured data. The way content spreads online has changed dramatically because these AI agents have reshaped how we find information.
Here, we will show you how to prepare your website for AI crawling and indexing. You’ll learn practical steps to keep your website visible as AI reshapes the search landscape. The guide covers everything from technical fixes to content structure and ways to optimize your crawl budget.
Understand How AI Crawlers Work
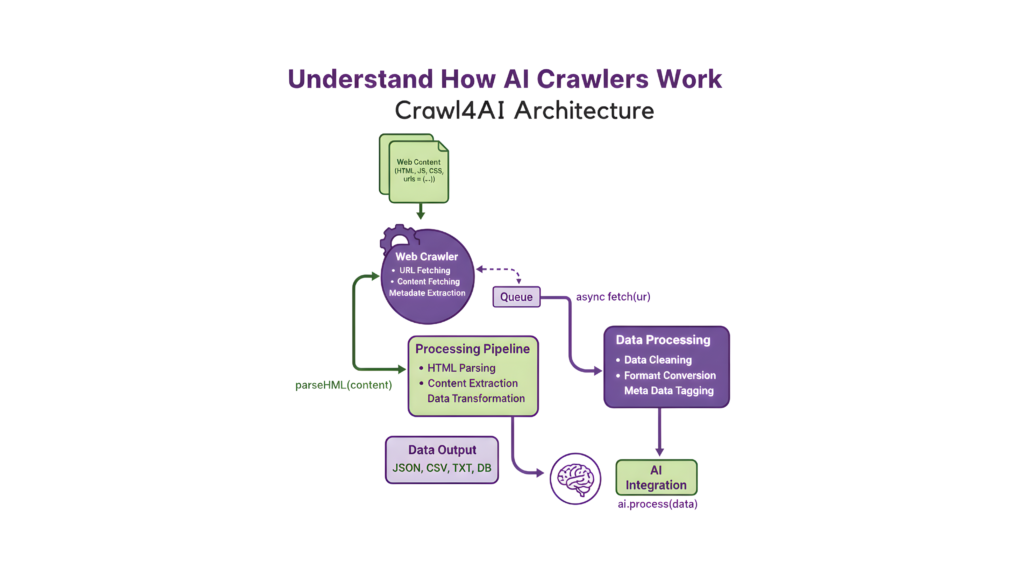
Image Source: Cobus Greyling – Medium
Web crawlers help determine website visibility, and they’ve been doing it for decades. AI crawlers scan and interpret your content in completely new ways these days.
What is Crawling In The Website Context?
Web crawling happens when automated bots navigate through websites to collect and catalog information. These bots find and analyze your web pages. They follow links, download content, and store data in their indexes.
Bots like Googlebot and Bingbot do this work to figure out what shows up in search engine results pages (SERPs). Your site’s ranking and organic traffic depend on how well these bots can crawl your pages.
Crawlers do several things when they visit your site:
- Find new pages through internal linking and sitemaps
- Analyze content to check relevance and quality
- Store information in their indexes
- Figure out how your content appears in results
Bots generate about 30% of global web traffic, and this is a big deal as it means that human internet traffic is in some places. You just need to learn this process to keep your website visible as search technology changes.
How AI Crawlers Differ From Traditional Bots
Traditional search engine crawlers index your content to bring traffic back to your site. AI crawlers are different – they collect data to give direct answers and sometimes skip your website completely. This changes everything about the value of being crawled.
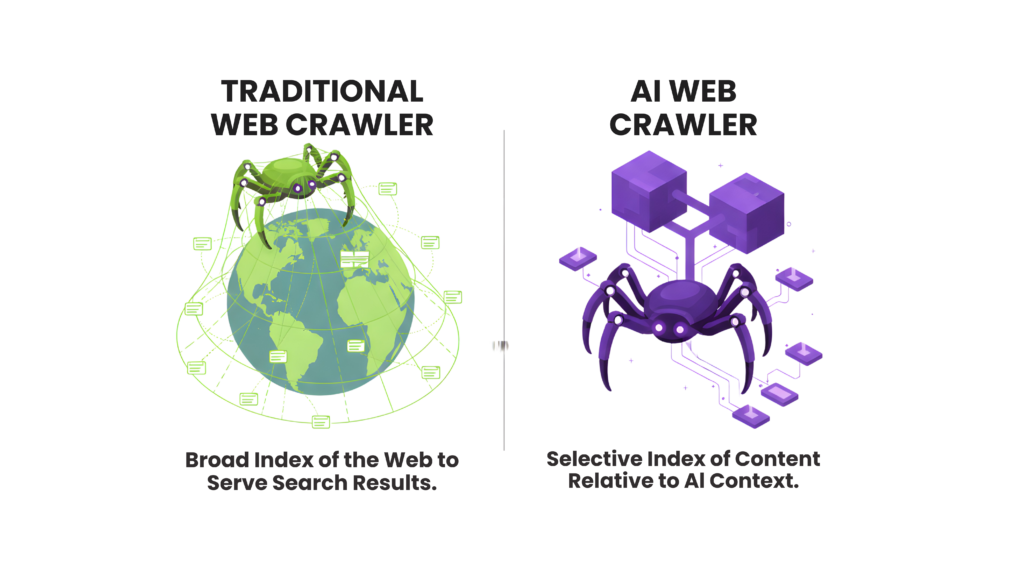
Key differences include:
Traditional search crawlers look at keyword matching and pull out metadata. AI-powered crawlers use advanced natural language processing to learn context, sentiment, and deeper meanings. On top of that, traditional crawlers can run JavaScript with some limits, but most AI crawlers can’t run JavaScript at all.
Your site’s dynamic content might be invisible to AI crawlers because of this technical limit. This includes pop-ups, interactive charts, infinite scroll elements, or content behind clickable tabs. To name just one example, see OpenAI’s GPTBot – it only reads raw HTML content that’s visible when the page first loads.
The core team sees huge differences in resource use. Some AI crawlers show a 38,000:1 crawl-to-referral ratio compared to regular search engines. This means their bots might scan tens of thousands of pages to send just one visitor back to your website.
Types of AI Crawlers: Training Vs Real-Time
You should know about the three main types of AI crawlers:
1. AI Training Bots scan the web all the time to collect massive amounts of data for training large language models. GPTBot (OpenAI), ClaudeBot (Anthropic), and Meta-ExternalAgent (Meta) are good examples. These bots make up nearly 80% of all AI crawler activity, up from 72% a year ago. They use lots of server resources because they crawl deeply and often through websites.
2. AI Indexing Bots create special search indexes that work better for AI applications. OAI-SearchBot (OpenAI), Claude-SearchBot (Anthropic), and PerplexityBot (Perplexity AI) fall into this category. They’ve been responsible for about 18% of AI crawling in the last 12 months, though that number has dropped to about 15% recently.
3. On-Demand/Retrieval Bots spring into action when users ask AI platforms questions that need immediate information. ChatGPT-User (OpenAI), Claude-User (Anthropic), and Perplexity-User (Perplexity AI) are examples. They make specific requests to websites when users ask about things beyond the AI’s training data, making up just 2-3% of AI crawler traffic.
These differences matter because each type of crawler interacts with your content uniquely. Training crawlers might visit every few weeks, while retrieval bots jump into action the moment users ask about your brand or products.
Fix Technical Barriers to AI Indexing
Your website might be invisible to AI crawlers due to technical barriers, even with excellent content. Studies show that about 25% of AI crawlers can fetch JavaScript but fail to execute it. This makes your dynamic content hard to reach.
Avoid JavaScript Rendering Issues
JavaScript handling creates the biggest gap between search engines and AI crawlers. Google’s AI crawler (used by Gemini) handles JavaScript well through a shared Web Rendering Service, according to Martin Splitt. Most other AI crawlers don’t execute JavaScript – including those from OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, and Common Crawl.
This creates a bigger issue. Your site’s core content becomes invisible to both the foundation layer and live AI crawling when it depends on JavaScript. Here’s how to fix this:
- Put essential content in the original HTML response
- Add features progressively instead of making them JavaScript-dependent
- Turn off JavaScript to see what AI crawlers notice on your site
Ensure Clean And Available URLs
Your URL structure can affect how well AI systems crawl your site. Let’s make your content more visible:
You should build a logical site structure with categories that guide crawlers smoothly. Technical SEO experts suggest making key pages available within three clicks from the homepage.
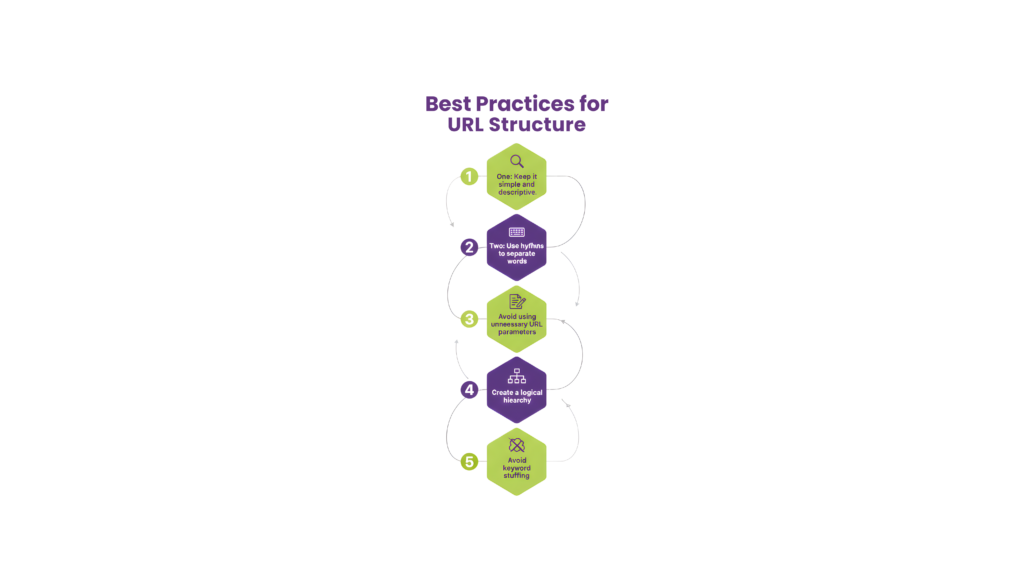
Make all URL versions consistent by fixing trailing slashes, HTTP/HTTPS differences, and duplicate URLs with parameters using canonical tags. Keep URLs clear and brief—short, meaningful URLs work better for both traditional SEO and AI parsing.
Use Server-Side Rendering Or Prerender.io
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) sends complete HTML pages to browsers and crawlers without JavaScript execution. Content-focused websites benefit from this approach.
Prerender.io offers another solution to bridge this gap. Here’s how it works:
- It spots when a crawler visits your site
- Sends a pre-rendered, static HTML version to the crawler
- Keeps the dynamic JavaScript experience for regular users
One client saw an 800% increase in referral traffic from ChatGPT after using Prerender.io. Sites that take 30-60 seconds to render can speed up crawling dramatically with Prerender.io.
Optimize Crawl Budget For Large Sites
Crawl budget becomes crucial for websites with thousands or millions of pages. It represents Google’s time and resource allocation for crawling your site.
Crawl capacity limit and crawl demand determine your crawl budget. You can optimize this resource:
Block unnecessary URLs with robots.txt to save crawler time on shopping carts, parameter links, or backend areas. Fix duplicate structures by standardizing URL versions and adding canonical tags.
Watch your crawl efficiency through Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report. Large sites with frequent updates should use dynamic rendering to reduce the rendering load on crawl budget. JavaScript-heavy sites typically use 9 times more rendering resources than server-rendered pages.
These technical fixes will help AI crawlers access, understand, and index your content better. Your website will get the visibility it deserves in this new era of AI-powered search.
Make Your Content Machine-Readable
AI crawlers now drive much of the search traffic, so your content must be machine-readable. Your valuable content stays invisible to AI systems without the right formatting and markup.
Add Structured Data Using Schema.Org
Schema.org offers a standardized vocabulary that makes your content understandable to both humans and machines. Schema markup acts like digital labels that help AI crawlers understand what your content means—not just its appearance.
The right schema markup makes your website eligible for rich results in search engines and helps with better AI crawling. Results speak for themselves—Rotten Tomatoes saw a 25% higher click-through rate on pages with structured data.
Here’s how to add schema markup the right way:
- Use JSON-LD format (placed in the <head> or <body> section) since major search engines and AI systems prefer it
- Add all required properties for each schema type
- Make sure your markup matches visible page content
- Check your schema using Google’s Rich Results Test
Use Clear Metadata And Headings
AI systems need proper metadata to understand your content’s purpose and relevance. You should focus on:
Start with simple SEO tags like <title>, <meta description>, and semantic HTML elements (<article>, <section>, <nav>). Next, add OpenGraph tags so your content looks better when shared on different platforms.
A logical heading structure (H1-H6) shows your content’s hierarchy. This helps AI crawlers spot main topics and supporting details—especially important when AI models try to find answers in your content.
Create Extractable Content Blocks
Your content needs distinct, meaningful components to be machine-readable. Content engineering breaks down information into reusable, structured, and format-free blocks.
Structured content separates meaning from presentation. You should organize information into defined fields that machines can process easily. Yes, it is an approach that helps both AI systems and human readers digest information better.
Include Recency Signals Like Last Updated
AI systems love fresh content when choosing what to show in results. Your relevant content might get overlooked for newer material if it lacks clear timestamps.
Make use of this recency preference:
- Put visible “last updated” dates on key pages
- Keep your dateModified and datePublished properties current in schema markup
- Set up automatic timestamp updates for major changes
Research shows that posts with visible “Last updated” dates get more clicks because people and algorithms trust newer information. Of course, this detail can boost your content’s visibility to AI systems.
Control and Guide AI Access
AI access control for your website requires more than basic allow/deny decisions. AI bot requests have surged by 300% in the first half of 2025. This surge makes access management crucial.
Configure Robots.txt For AI Agents
The robots.txt file acts as your first defense line against AI crawler access. Here’s how to make it work:
- List AI crawlers by their unique user-agent names (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended)
- Set up custom rules for different bot types based on your content strategy
- Control access precisely by allowing or disallowing specific directories
A smart approach would be to let search and user-triggered crawlers through while blocking training bots that don’t generate referral traffic.
Use Llms.txt to Highlight Key Resources
The llms.txt standard, which emerged in autumn 2024, is a chance to guide AI systems to your valuable content. This Markdown file works like a roadmap for AI crawlers and helps them understand your site quickly.
Add this file to your root directory with:
- A brief table of contents linking to key resources
- Project summaries and section overviews that are easy to follow
- Links to your most important pages are organized clearly
Avoid Blocking AI Crawlers Unintentionally
Your robots.txt files might block legitimate crawlers if not set up right. Before you start blocking anything, keep in mind that AI bots serve different purposes – some drive valuable traffic while others just drain resources.
Check your access rules often to stay visible in AI-powered search and protect content as needed. It’s worth mentioning that traditional defenses like robots.txt follow voluntary protocols, and some questionable bots might ignore them completely.
Future-Proof With Personalization and Task Flows
Personalization leads AI-friendly website strategies. AI crawlers have become more sophisticated, and they give priority to content that answers user questions directly while providing clear task instructions.
Arrange Content With Your ICP’s Questions
Your website’s AI visibility improves when you create content that matches your Ideal Customer Profile’s (ICP) questions. Your ICP acts as a stand-in for actual customers—it doesn’t replace direct customer feedback but helps you refine messaging without constant customer interruptions. You should analyze customer call transcripts, support logs, and survey data to find recurring questions. The content structure should address these questions using your customers’ exact language.
Add Step-By-Step Task Instructions
AI search engines prefer content with clear, practical guidance. Your focus should extend beyond keywords to address specific user problems with step-by-step solutions. Create structured task flows on important pages that guide users through your service-related processes. Well-laid-out task instructions help human visitors and AI systems understand your expertise better.
Use Schema Types Like Howto And FAQPage
The FAQPage schema has become one of the most powerful structured data types to optimize for AI search. This markup sends a clear message to AI platforms: “This is a question. This is the authoritative answer”. Each page should include 5-10 FAQ questions with 40-60-word responses that contain specific data and examples. HowTo schema tells AI crawlers that your task-oriented content offers valuable instructions.
Keep Consistency Across Feeds And Listings
Channel consistency matters for both customers and AI systems. 41% of consumers list inconsistent customer service answers as their biggest frustration. Content-specific guidelines will give AI-friendly uniformity across your website, knowledge base, and support materials.
Monitor AI Bot Activity And Visibility
Log file analysis reveals which AI bots visit your site, what pages they access, and their frequency. You can spot potential crawling issues like repeated requests, error codes, incomplete crawls, or timeout patterns. Track changes in AI bot traffic patterns to measure how well your optimization efforts work and maintain visibility as AI technology evolves.
Conclusion
AI crawlers have altered the map of search, making your website’s technical foundation vital to maintain visibility. This piece shows how these intelligent bots work differently from their traditional counterparts. They handle JavaScript and dynamic content in unique ways.
Technical readiness is the lifeblood of AI visibility. Your content might stay invisible to AI systems, whatever its quality, without proper server-side rendering, clean URL structures, and optimized crawl budgets. A website with machine-readable content and appropriate schema markup becomes a structured knowledge resource that AI systems can process well.
Now is the perfect time to adapt. Search data proves that AI crawling has substantial advantages in visibility. Your competitors won’t wait, so taking action today will secure your digital presence for tomorrow.
Do you need expert help to implement these AI-ready strategies? RankFast’s complete SEO for healthcare services can turn your website into an AI-friendly knowledge hub. Our team will give a strong digital presence that stays proactive with evolving search technologies. We offer technical fixes, content restructuring, and complete search marketing for specialized industries like healthcare SEO services.
Start by checking your current online strength with our free Bulk Domain Authority Checker and take the first step to future-proof your website today.
FAQs
Q1. How do AI crawlers differ from traditional search engine bots?
AI crawlers use advanced natural language processing to understand context and meaning, while traditional bots focus on keyword matching. Most AI crawlers can’t execute JavaScript, limiting their ability to see dynamic content. They also have different resource consumption patterns, often crawling more pages per referral than traditional search engines.
Q2. What are the main types of AI crawlers?
There are three primary types: AI Training Bots that collect data for training language models, AI Indexing Bots that build specialized search indexes, and On-Demand/Retrieval Bots that activate for real-time user queries. Each type interacts with websites differently and serves distinct purposes in the AI ecosystem.
Q3. How can I make my website more accessible to AI crawlers?
Ensure critical content is in the initial HTML response, use server-side rendering or solutions like Prerender.io, maintain clean and accessible URLs, and implement structured data using Schema.org. Also, optimize your crawl budget by blocking low-value URLs and fixing structural redundancies.
Q4. What is the importance of structured data for AI crawling?
Structured data using Schema.org vocabulary helps AI crawlers understand your content’s meaning and context. It makes your website eligible for rich results in search engines and improves AI crawling efficiency. Implementing structured data can lead to higher click-through rates and better visibility in AI-powered search results.
Q5. How can I control AI access to my website?
Use robots.txt to specify rules for different AI crawlers, implement the new llms.txt standard to guide AI systems to your most valuable content, and regularly review your access rules. Be cautious not to unintentionally block legitimate AI crawlers that may bring valuable traffic to your site.

Leave a Reply